List of aperiodic sets of tiles
In geometry, a tiling is a family of shapes – called tiles – that cover the plane (or any other geometric setting) without gaps or overlaps.[1] Such a tiling might be constructible from a single fundamental unit or primitive cell and is then called periodic.[2] An example of such a tiling is shown in the diagram to the right (see the image description for more information). Every periodic tiling has a primitive cell that can generate it. A tiling that cannot be constructed from a single primitive cell is called nonperiodic. If a given set of tiles allows only nonperiodic tilings, then this set of tiles is called aperiodic.[3] The tilings obtained from an aperiodic set of tiles can be called aperiodic tilings.
The first table explains the abbreviations used in the second table. The second table contains all known aperiodic sets of tiles and gives some additional basic information about each set. Please note that this list of tiles is still incomplete.
Contents |
Explanations
| Abbreviation | Meaning | Explanation |
|---|---|---|
| E2 | Euclidean plane | normal flat plane |
| H2 | hyperbolic plane | plane, where the parallel postulate does not hold |
| E3 | Euclidean 3 space | space defined by three perpendicular coordinate axes |
| MLD | Mutually locally derivable | two tilings are said to be mutually locally derivable from each other, if one tiling can be obtained from the other by a simple local rule (such as deleting or inserting an edge) |
List
| Image | Name | Number of tiles | Space | Publication Date | refs | Comments |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Trilobite and cross tiles | 2 | E2 | 1999 | [4] | Tilings MLD from the chair tilings | |
| Penrose P1 tiles | 6 | E2 | 1974[Note 1] | [5] | Tilings MLD from the tilings by P2 and P3, Robinson triangles, and "Starfish, ivy leaf, hex" | |
| Penrose P2 tiles | 2 | E2 | 1977[Note 2] | [6] | Tilings MLD from the tilings by P1 and P3, Robinson triangles, and "Starfish, ivy leaf, hex" | |
| Penrose P3 tiles | 2 | E2 | 1978[Note 3] | [7] | Tilings MLD from the tilings by P1 and P2, Robinson triangles, and "Starfish, ivy leaf, hex" | |
| Binary tiles | 2 | E2 | 1988 | [8][9] | Although similar in shape to the P3 tiles, the tilings are not MLD from each other, developed in an attempt to model the atomic arrangement in binary alloys | |
| Robinson tiles | 6 | E2 | 1971[Note 4] | [10] | Tiles enforce aperiodicity by forming an infinite hierarchy of square lattices | |
| No image | Ammann A1 tiles | 6 | E2 | 1977[11] | [12] | Tiles enforce aperiodicity by forming an infinite hierarchal binary tree. |
| Ammann A2 tiles | 2 | E2 | 1986[Note 5] | [13] | ||
| Ammann A3 tiles | 3 | E2 | 1986[Note 5] | [13] | ||
| Ammann A4 tiles | 2 | E2 | 1986[Note 5] | [13][14] | Tilings MLD with Ammann A5. | |
| Ammann A5 tiles | 2 | E2 | 1982[Note 6] | [15][16] | Tilings MLD with Ammann A4. | |
| No image | Penrose Hexagon-Triangle tiles | 2 | E2 | 1997[17] | [17][18] | |
| No image | Golden Triangle tiles | 10 | E2 | 2001 [19] | [20] | date is for discovery of matching rules. Dual to Ammann A2 |
| Socolar tiles | 3 | E2 | 1989[Note 7] | [21][22] | Tilings MLD from the tilings by the Shield tiles | |
| Shield tiles | 4 | E2 | 1988[Note 8] | [23][24] | Tilings MLD from the tilings by the Socolar tiles | |
| Square triangle tiles | 5 | E2 | 1986[25] | [26] | ||
| No image | Sphinx tiles | 91 | E2 | [27] | ||
| Starfish, ivy leaf and hex tiles | 3 | E2 | [28][29][30] | Tiling is MLD to Penrose P1, P2, P3, and Robinson triangles | ||
| Robinson triangle | 4 | E2 | [12] | Tiling is MLD to Penrose P1, P2, P3, and "Starfish, ivy leaf, hex". | ||
| Danzer triangles | 6 | E2 | 1996[31] | [32] | ||
| Pinwheel tiles | E2 | 1994[33][34] | [35][36] | Date is for publication of matching rules. | ||
| No image | Wang tiles | 104 | E2 | 2008[Note O] | [37] | |
| No image | Wang tiles | 56 | E2 | 1971[Note 4] | [38] | Tiles enforce aperiodicity by forming an infinite hierarchy of square lattices |
| Wang tiles | 32 | E2 | [39] | |||
| Wang tiles | 16 | E2 | [40][41] | |||
| Wang tiles | 14 | E2 | [42] | |||
| Wang tiles | 13 | E2 | 1996 | [43][44] | ||
| No image | Decagonal Sponge tile | 1 | E2 | 2002 | [45][46] | Porous tile consisting of non-overlapping point sets |
| No image | Horocyclic tiles | 85 | H2 | 2005 | [47] | |
| Goodman-Strauss hyperbolic tile | 1 | H2 | 2005 | [48] | Weakly aperiodic | |
| No image | Goodman-Strauss strongly aperiodic tiles | 26 | H2 | 2005 | [48] | |
| No image | Böröczky tile | 1 | Hn | 1974[49] | [50] | Not strongly aperiodic |
| No image | Schmitt tile | 1 | E3 | 1988 | [51] | Screw-periodic |
| Schmitt-Conway-Danzer tile | 1 | E3 | [51] | Screw-periodic and convex | ||
| Socolar Taylor tile | 1 | E3 | 2010 | [52][53] | Periodic in third dimension | |
| No image | Penrose rhombohedra | 2 | E3 | 1981[54] | [55][56][57][58][59][60][61] | |
| No image | Wang cubes | 21 | E3 | [62] | ||
| No image | Wang cubes | 18 | E3 | [63] | ||
| No image | Wang cubes | 16 | E3 | [64] | ||
| No image | Danzer tetrahedra | 4 | E3 | 1989[65] | [66] | |
| I and L tiles | 2 | En for all n ≥ 3 | 1999 | [67] |
Notes
First published in
- 1.^ Penrose, R. (1974), "The role of Aesthetics in Pure and Applied Mathematical Research", Bull. Inst. Math. and its Appl. 10: 266-271
- 2.^ Gardner, M. (January 1977), "Extraordinary nonperiodic tiling that enriches the theory of tiles", Scientific American 236: 110-121
- 3.^ Penrose, R. (1978), "Pentaplexity", Eureka 39: 16-22
- 4.^ Robinson, R. (1971), "Undecidability and nonperiodicity of tilings in the plane", Inv. Math. 12: 177-209
- 5.^ Grünbaum, B.; Shephard, G. C. (1986), Tilings and Patterns, New York: W. H. Freeman, ISBN 0-7167-1194-X.
- 6.^ Beenker, F. P. M.(1982), "Algebraic theory of non-periodic tilings of the plane by two simple building blocks: a square and a rhombus", Eindhoven University of Technology, TH Report 82-WSK04
- 7.^ Socolar, J. E. S. (1989), "Simple octagonal and dodecagonal quasicrystals", Phys. Rev. A 39: 10519-51
- 8.^ Gähler, F., "Crystallography of dodecagonal quasicrystals", published in Janot, C.: Quasicrystalline materials : Proceedings of the I.L.L. / Codest Workshop, Grenoble, 21–25 March 1988. Singapore : World Scientific, 1988, 272-284
References
- ^ Grünbaum B., Shephard G. C. (1977), "Tilings by Regular Polygons", Math. Mag. 50 (5): 227–247, doi:10.2307/2689529, http://vohweb.chem.ucla.edu/voh/classes%5Cspring10%5CM117%20HNRS%20M180ID22%5CGrunbaumShephardTilingByRegPolygons.pdf.(archived at WebCite)
- ^ Edwards S., Fundamental Regions and Primitive cells (archived at WebCite)
- ^ Ollinger N. Mathematica in action (see page 268)
- ^ Goodman-Strauss C. (1999), "A Small Aperiodic Set of Planar Tiles", European J. Combinatorics 20 (5): 375–384, doi:10.1006/eujc.1998.0281 (preprint available here)
- ^ Mikhael J. Colloidal Monolayers On Quasiperiodic Laser Fields (see page 23) (archived at WebCite)
- ^ Gardner M. Penrose tiles to trapdoor ciphers (see page 86) (archived at WebCite)
- ^ Penrose R. (1979/80), "Pentaplexity", Math. Intell. 2: 32–37, http://www.ma.utexas.edu/users/radin/pentaplexity.html.(archived at WebCite)
- ^ Lançon F., Billard L. (1988), "Two-dimensional system with a quasi-crystalline ground state", J. Phys. France 49 (2): 249–256, doi:10.1051/jphys:01988004902024900, http://hal.archives-ouvertes.fr/docs/00/21/06/91/PDF/ajp-jphys_1988_49_2_249_0.pdf. (archived at WebCite)
- ^ Lançon F., Billard L. (1992), "A simple example of a non-Pisot tiling with five-fold symmetry", J. Phys. I France 2 (2): 207–220, doi:10.1051/jp1:1992134, http://hal.archives-ouvertes.fr/docs/00/24/64/73/PDF/ajp-jp1v2p207.pdf.(archived at WebCite)
- ^ Goodman-Strauss C. (1999), "Aperiodic Hierarchical tilings", Proc. of NATO-ASI "Foams, Emulsions, and Cellular Materials" Ser. E 354: 481–496, http://www.webcitation.org/5sxslGkXb.
- ^ Gardner, Martin (2001). The Colossal Book of Mathematics. W. W. Norton & Company. p. 76.
- ^ a b Grünbaum B. and Shephard G. C.. Tilings and Patterns., according to [1]; cf [2]
- ^ a b c Ammann R., Grünbaum B. and Shephard G. C. (1992), "Aperiodic Tiles", Discrete Comp Geom 8: 1–25, doi:10.1007/BF02293033, http://www.webcitation.org/5rjblcapr.
- ^ Harris E., Frettlöh D. Ammann A4
- ^ Komatsu K., Nomakuchi K., Sakamoto K., Tokitou T. (2004), "Representation of Ammann-Beenker tilings by an automaton", Nihonkai Math. J. 15: 109–118, http://projecteuclid.org/DPubS/Repository/1.0/Disseminate?view=body&id=pdf_1&handle=euclid.nihmj/1273779794.(archived at WebCite)
- ^ Harris E., Frettlöh D. Ammann-Beenker
- ^ a b Penrose R. (1997), "Remarks on tiling: Details of a (1+ε+ε2) aperiodic set.", Nato Asi Series C 489 The Mathematics of Long-Range Aperiodic Order: 467–497, ISBN 9780792345060, http://books.google.com/?id=3YGXr_nQFw8C&printsec=frontcover&dq=quasicrystals+and+geometry#v=onepage&q=quasicrystals%20and%20geometry&f=false.
- ^ Goodman-Strauss C., An aperiodic pair of tiles
- ^ Danzer, Ludwig; van Ophuysen, Gerrit (2001). "A species of planar triangular tilings with inflation factor
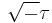 ". Res. Bull. Panjab Univ. Sci. 50 (1-4): 137–175. doi:2003f:52015.
". Res. Bull. Panjab Univ. Sci. 50 (1-4): 137–175. doi:2003f:52015. - ^ Gelbrich, G (1997). "Fractal Penrose tiles II. Tiles with fractal boundary as duals of Penrose triangles". Aequationes Math. 54: 108–116. MRMR1466298.
- ^ Gähler F., Lück R., Ben-Abraham S. I., Gummelt P.Dodecagonal tilings as maximal cluster coverings (archived at WebCite)
- ^ The Socolar tiling
- ^ Gähler F., Frettlöh D. Shield
- ^ Gähler F. (1993), "Matching rules for quasicrystals: the composition-decomposition method", J. of Non-crystalline Solids 153&154: 160–164, http://elib.uni-stuttgart.de/opus/volltexte/2009/3989/pdf/gaeh11.pdf.(archived at WebCite)
- ^ Stampfli, P (1986). "A Dodecagonal Quasiperiodic Lattice in Two Dimensions". Helv. Phys. Acta. 59: 1260–1263.
- ^ Hermisson J., Richard C., Baake M. A Guide to the Symmetry Structure of Quasiperiodic Tiling Classes (archived at WebCite)
- ^ Goodman-Strauss C., Aperiodic tilings (see page 74)
- ^ Lord E. A. (1991), "Quasicrystals and Penrose patterns", Current Science 61: 315, http://www.webcitation.org/5t3XY5gd3.
- ^ Olamy Z., Kléman M. (1989), "A two dimensional aperiodic dense tiling", J. Phys. France 50: 19–33, doi:10.1051/jphys:0198900500101900, http://hal.archives-ouvertes.fr/docs/00/21/08/96/PDF/ajp-jphys_1989_50_1_19_0.pdf. (archived at WebCite)
- ^ Mihalkovič M., Henley C. L., Widom M. (2004), "Combined energy-diffraction data refinement of decagonal AlNiCo", J. Non-Cryst. Solids 334&335: 177–183, http://people.ccmr.cornell.edu/~clh/PUBS/dfit-04.pdf. (archived at WebCite)
- ^ Nischke, K-P and Danzer, L, "A construction of inflation rules based on $n$-fold symmetry". Discrete Comput. Geom. 15 (2): 221–236. 1996. 96j:52035
- ^ Hayashi H., Kawachi Y., Komatsu K., Konda A., Kurozoe M., Nakano F., Odawara N., Onda R., Sugio A., Yamauchi M. Abstract:Notes on vertex atlas of planar Danzer tiling
- ^ Radin, C (1994). "The pinwheel tilings of the plane". Annals of Mathematics(2) 139 (3): 661–702. doi:10.2307/2118575. JSTOR 2118575. MR95d:52021. http://citeseerx.ist.psu.edu/viewdoc/summary?doi=10.1.1.44.9723&rank=1. Retrieved 2010-04-03.
- ^ Charles Radin (1994). "Symmetry Of Tilings Of The Plane". Annals of Math. http://citeseerx.ist.psu.edu/viewdoc/summary?doi=10.1.1.45.5319&rank=6. Retrieved 2010-04-03.
- ^ Radin, C; Wolff, M (1992). "Space tilings and local isomorphism". Geom. Dedicata 42 (3): 355–360. MR1164542.
- ^ Radin, C (1997). "Aperiodic tilings, ergodic theory, and rotations". The mathematics of long-range aperiodic order. Kluwer Acad. Publ., Dordrecht. MR1460035.
- ^ Ollinger N. Two-by-two Substitution systems and the Undecidability of the Domino Problem (see pages 476-485)
- ^ Kari, J.; Papasoglu, P. (1999). "Deterministic Aperiodic Tile Sets". Geometric and Functional Analysis 9: 353–369.
- ^ Lagae A., Kari J., Dutré P. (2006), "Aperiodic Sets of Square Tiles with Colored Corners", Report CW 460: 12, http://citeseerx.ist.psu.edu/viewdoc/download;jsessionid=9F2387ADDE287538436CC970669B4ABC?doi=10.1.1.89.1294&rep=rep1&type=pdf.(archived at WebCite)
- ^ Grünbaum, B.; Shephard, G. C. (1986), Tilings and Patterns, New York: W. H. Freeman, ISBN 0-7167-1194-X
- ^ Carbone, A.; Gromov, M.; Prusinkiewicz, P. (2000), Pattern Formation in Biology, Vision and Dynamics, Singapore: World Scientific Publishing Co. Pte. Ltd., ISBN 9810237928
- ^ Lagae A. Tile Based Methods in Computer Graphics Dissertation (see page 149) (archived at WebCite)
- ^ Culik K., Kari J. On aperiodic sets of Wang tiles
- ^ Culik K. An aperiodic set of 13 Wang tiles (archived at WebCite)
- ^ Zhu F. The Search for a Universal Tile
- ^ Bailey D. A., Zhu F. A Sponge-Like (Almost) Universal Tile
- ^ Goodman-Strauss C., A hierarchical strongly aperiodic set of tiles in the hyperbolic plane
- ^ a b Goodman-Strauss C. (2005), "A strongly aperiodic set of tiles in the hyperbolic plane", Invent. Math. 159: 120, Bibcode 2004InMat.159..119G, doi:10.1007/s00222-004-0384-1
- ^ Böröczky, K. (1974), "Gömbkitöltések állandó görbületü terekben I", Mat. Lapok. 25: 265–306.Böröczky, K. (1974), "Gömbkitöltések állandó görbületü terekben II", Mat. Lapok. 26: 67–90.
- ^ Dolbilin N., Frettlöh D. Properties of Böröczky tilings in high dimensional hyperbolic spaces (archived at WebCite)
- ^ a b Radin, Charles (1995), "Aperiodic tilings in higher dimensions" (fee required), Proceedings of the American Mathematical Society (American Mathematical Society) 123 (11): 3543–3548, doi:10.2307/2161105, JSTOR 2161105.
- ^ Socolar J. E. S. and Taylor J. M. An aperiodic hexagonal tile
- ^ Socolar J. E. S. and Taylor J. M. Forcing nonperiodicity with a single tile
- ^ Mackay A. L. (1981), "De Nive Quinquangula: On the pentagonal snowflake", Sov. Phys. Crystallogr. 26(5): 517–522, http://materials.iisc.ernet.in/~lord/webfiles/Alan/CV073eng.pdf. (archived at WebCite)
- ^ Meisterernst G. Experimente zur Wachstumskinetik Dekagonaler Quasikristalle (Experiments on the growth kinetics of decagonal quasicrystals) Dissertation (see page 18-19) (archived at WebCite)
- ^ Jirong S. (1993), "Structure Transition of the Three-Dimensional Penrose Tiling Under Phason Strain Field", Chinese Phys. Lett. 10, No.8: 449–452, http://cpl.iphy.ac.cn/qikan/manage/wenzhang/0100449.pdf. (archived at WebCite)
- ^ Inchbald G. A 3-D Quasicrystal Structure
- ^ Lord E. A., Ranganathan S., Kulkarni U. D. (2001), "Quasicrystals: tiling versus clustering", Phil. Mag. A 81: 2645–2651, http://materials.iisc.ernet.in/~lord/webfiles/pmq.pdf. (archived at WebCite)
- ^ Rudhart C. P. Zur numerischen Simulation des Bruchs von Quasikristallen (On the numeric simulation of cracking in quasicrystals) see page 11
- ^ Lord E. A., Ranganathan S., Kulkarni U. D. (2000), "Tilings, coverings, clusters and quasicrystals", Current Science 78, No.1: 64–72, http://materials.iisc.ernet.in/~lord/webfiles/eric/pdfs/55.pdf. (archived at WebCite)
- ^ Katz A. (1988), "Theory of Matching Rules for the 3-Dimensional Penrose Tilings", Commun. Math. Phys. 118 (2): 263–288, doi:10.1007/BF01218580, http://projecteuclid.org/DPubS/Repository/1.0/Disseminate?view=body&id=pdf_1&handle=euclid.cmp/1104161989. (archived at WebCite)
- ^ Culik K., Kari J. An aperiodic set of Wang cubes
- ^ Walther, G.; Selter, C. (1999), Mathematikdidaktik als design science, Leipzig: Ernst Klett Grundschulverlag, ISBN 3-12-2000060-1
- ^ Lu A., Ebert D. S., Qiao W., Kraus M., Mora B. Interactive volume illustration using Wang cubes
- ^ Danzer, L. (1989), "Three-Dimensional Analogs of the Planar Penrose Tilings and Quasicrystals.", Discrete Mathematics 76: 1–7, doi:10.1016/0012-365X(89)90282-3
- ^ Zerhusen A., Danzer's three dimensional tiling
- ^ Goodman-Strauss C. (1999), "An Aperiodic Pair of Tiles in En for all n ≥ 3", Europ. J. Combinatorics 20 (5): 385–395, doi:10.1006/eujc.1998.0282 (preprint available here)
External links
- Stephens P. W., Goldman A. I. The Structure of Quasicrystals
- Levine D., Steinhardt P. J. Quasicrystals I Definition and structure